To achieve the elimination or reduction of viral hepatitis by 2030, strategic training of healthcare professionals is a key step.

The second phase of the project will focus on training, education & increase in vaccination against Hepatitis.
The project aims to initiate trainings for healthcare professionals in a manner:
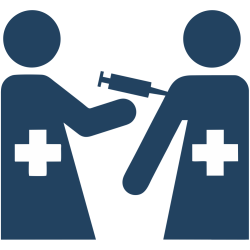
The program aims to award institutions as ‘Viral Hepatitis Champions’ who achieve at least a minimum of 90% vaccination status among HCWs working in their institute and have a strong set of compliance towards infection prevention and control practices.
Healthcare staff completing vaccine schedule will be awarded certificate duly recognized by ILBS & WHOCC.
IEC is an effective medium for bringing awareness, providing information, eradicating mythical beliefs, and championing the cause for health and development. In the health sector, IEC plays a pivotal role in spreading awareness and taking preventive measures.
Project aims at creating IEC for display across healthcare institutions in blood banks, OPDs, patient wards, laboratories to create awareness regarding viral hepatitis along with universal precaution guidelines.

The project aims at achieving below mentioned goals at the end of the program:


Call us now

Drop us an email
Monday to Saturday
